Genotyping of transgenic mice models
Quantitative RT-PCR
Western Blot
Rodent Primary Neurons and Glia Culture
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
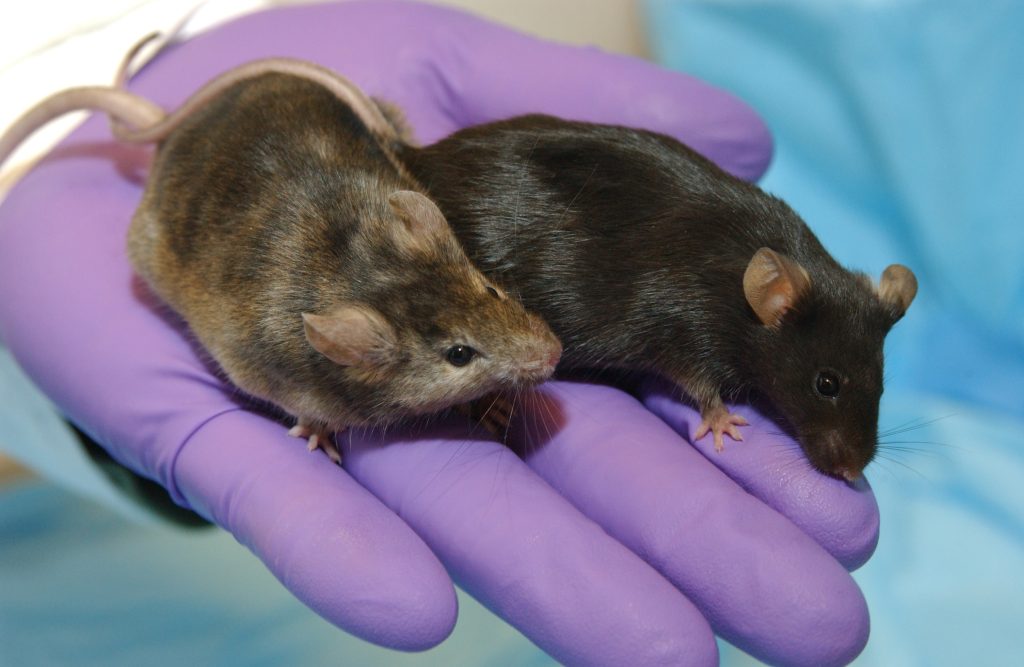
Genotyping of transgenic mice models
Transgenic mice are mouse models which have their genome altered through gene editing to include a foreign gene sequence, or transgene, and they are widely used in understanding human diseases, accelerating drug development, and evaluating potential therapies.
The use of transgenic mice models can avoid undesired immune responses; and help in understanding the significance of specific human drug-metabolizing enzymes in drug clearance and pharmacokinetics, and predicting potential drug-drug interactions and chemical toxicity in humans. These models are helpful in understanding the significance of a specific enzymes in drug metabolism, drug interactions, pharmacokinetics, dynamics and chemical toxicity.

Quantitative RT-PCR
RT-PCR is term used for “Reverse Transcription” PCR, where the starting genetic material in PCR process is RNA and RNA is first transcribed in reverse into its DNA complement by reverse transcriptase enzyme.
RT-PCR is used for viral drug sensitivity testing for slow-growing viruses that do not readily produce cytopathic effect, and they provide a rapid, comprehensive overview of how cells respond to new potential drugs.
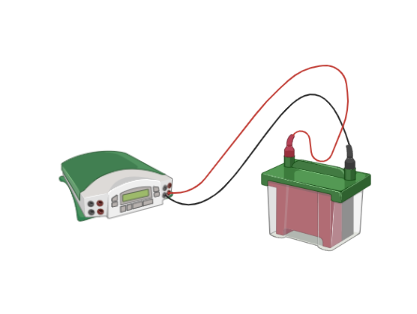
Western Blot
Western blot separates proteins by size and shape with an electric field applied to a gel, and then targeted proteins are stained with antibodies. It can be used to monitor protein levels, post-translational modifications, and to understand the mechanism of action for drugs.
Also, Western blots can be used to look for changes in proteins related to neurotransmitters and receptors related to drugs’ mechanism.
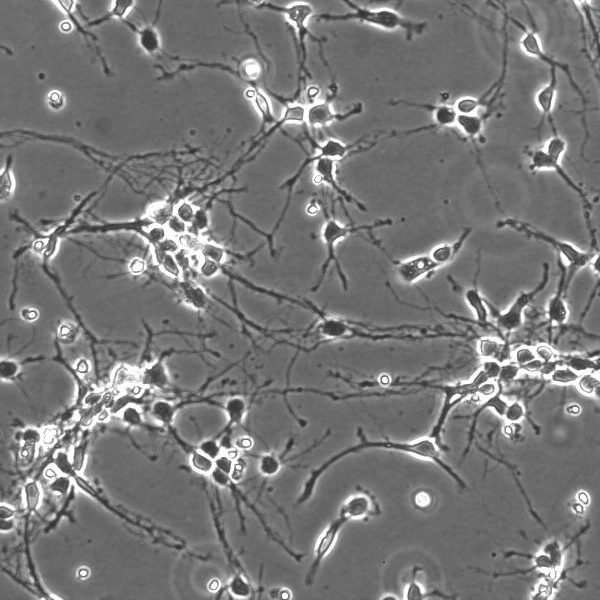
Rodent Primary Neurons and Glia Culture
Primary neuronal or glia cultures derived from wild-type or genetically engineered rodents is a tool to study mechanism of action and potential toxicity of compounds. Primary neurons also allow scientists to evaluate the effects of pharmaceutical agents. They are widely used to study the biological functions of microglia in vitro, hence the interactions between microglia and other brain cells.
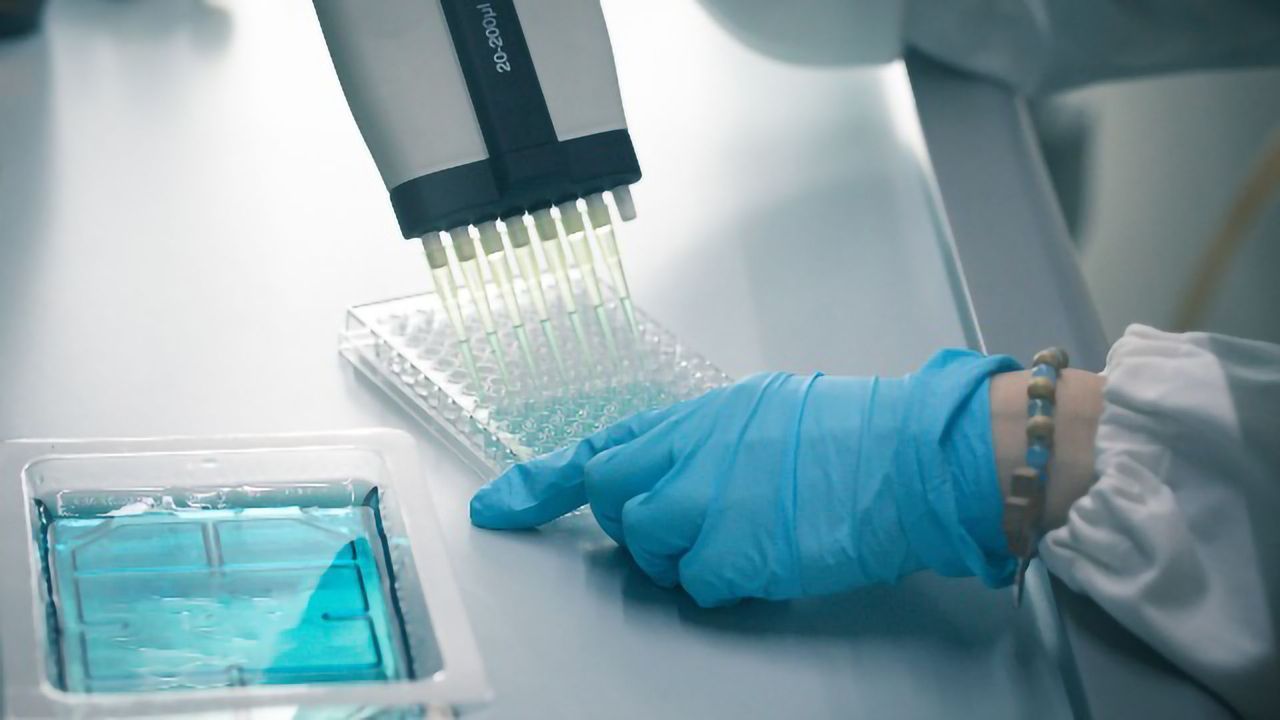

Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) screening techniques can be used for antibodies drug development studies. ELISAs are competition binding assays in which enzyme-linked drug competes with unlabaled drug for binding to anti-drug antibody.
ELISAs can specifically target a wide range of analytes using many different types of samples, and offer greater efficacy both in terms of cost and speed in real-world applications. They are a reliable and simple solution for drug testing.
