Anxiety and Depression
- Open Field Test
- Elevated Plus Maze Test
- Forced Swim Test
- Tail Suspension Test
- Sucrose Preference Test
Cognition
- Morris Water Maze (MWM) Test
- Barnes Maze Test
- Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test
Epilepsy and Seizure
- Epilepsy and Seizure Behavioural Test
Drug Abuse Liability
Motor Function
- Open Field Test
- EMG recording during treadmill walking
- Narrow Beam Test
- Pole Climbing Test
- Rotarod Test
- Grip Strength Test
Peripheral Nerve Regeneration Test
EMG recording during treadmill walking
EMG patterns during treadmill walking are used for analysing motor function activity of the mice after impalntation and after pharmacological treatment.
Narrow Beam Test
The beam walking test is used to access fine motor coordination and balance in rodents. The goal of beam walking test is for the subject to stay upright and walk across the narrow beam to a safe platform. Performance on the beam is quantified by measuring the time it takes for the subject to cross the beam and the speed of the subject. During the process, the activities of mice will be recorded by camera and analysed by ANY-Maze. This test is particularly used for detecting subtle deficits in motor skills and balance that may not be detected by other motor tests.
Pole Climbing Test
The pole climb test is widely used to assess basal ganglia related movement disorders in mice. The test evaluates the ability of a mouse to grasp and maneuver on a pole in order to descend to its home cage.
Mice are trained to complete the pole test over three training trials and are placed with their head oriented upward on top of the pole. The time required for the animals to orient themselves facing in a downward direction (time to T turn) and to descend to the base of the pole (total time) is recorded for three trials. Recordings start when the animal began the turning movement, and the footage will be analyzed by ANY-Maze.
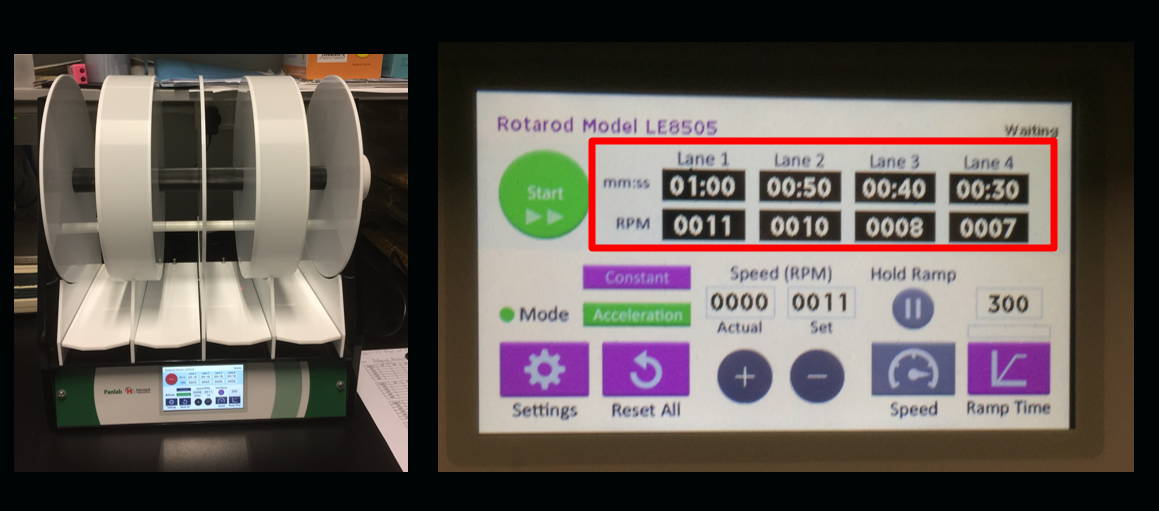
Rotarod Test
The rotarod test is widely used to evaluate the motor coordination of rodents, and is especially sensitive in detecting cerebellar dysfunction.
Open Field Test
Open-field experiments allow the evaluation of animal’s basal activity and its evolution, in response to novelty or anxiogenic environment, and in response to pharmacological treatment.
Assessment takes place in a square(49cm*49cm), black Plexiglas box. The subject is placed in the arena and allowed to freely move about for 10 minutes while being recorded by an overhead camera. The footage will then be analyzed by ANY-Maze, an automated tracking system for the following parameters: distance moved, velocity, and time spent in pre-defined zones. The Open Field test is useful for evaluating the effect of novel chemical entities on general activity.
Elevated Plus Maze Test
Elevated plus maze test is a widely used behavioral test for rodents to assess the anti-anxiety effects of pharmacological agents. Prescreening of newly developed pharmacological agents for treatment of anxiety-related disorders can be carried out using elevated plus maze test. Mice are placed at the junction of the four arms of the maze, facing an open arm and their activities are recorded by a video-tracking system. An increase in open arm activity reflects anti-anxiety behavior.
Forced Swim Test
The forced swim test (FST) is one of the most commonly used animal models for assessing antidepressant-like behavior. FST in rats will take place over 48 hours and followed by video analysis of the behavior. The FST involves the scoring of active (swimming and climbing) or passive (immobility) behavior when rodents are forced to swim in a cylinder from which there is no escape. The FST can be used for evaluation of antidepressant drugs, antidepressant efficacy of new compounds, and experimental manipulations that are aimed at rendering or preventing depressive-like states.
Tail Suspension Test
The tail-suspension test (TST) is a mouse behavioral test used in the screening of potential antidepressant drugs, and assessing of other manipulations that are expected to affect depression related behaviors. In TST, mice are suspended by their tails with tape, in a position that it cannot escape or hold on to nearby surfaces. The resulting escape oriented behaviors are quantified.
Sucrose Preference Test
Sucrose Preference Test (SPT) is a reward-based test which assesses the mouse’s interest in a sweet-tasting sucrose solution relative to unsweetened water, and is used as an indicator of anhedonia. Anhedonia is the inability to experience pleasure from rewarding or enjoyable activities, and is a core symptom of depression in humans, SPF is recommended for the evaluation of depressive behaviors in depression studies and anhedonia in mice.
Morris Water Maze (MWM) Test
Morris Water maze test is a widely-used test of spatial learning for rodents that relies on distal cues to navigate from start locations around the perimeter of an open swimming arena to locate a submerged escape platform. This test can be altered in different ways to investigate working memory, reference memory and task strategy. The use of water maze test in assessing learning and memory has been reviewed as it has the relationship between performance in the test and both neurotransmitter systems and drug effects.
Barnes Maze Test
The Barnes maze test is a dry-land based rodent behavioral paradigm for assessing spatial learning and memory. This test represents a well-established alternative to water maze and offers the advantage of being free from the potentially confounding influence of swimming behavior. It is useful for evaluating novel chemical entities for their effects on cognition and identifying cognitive deficits in transgenic strains of mice, especially those prone to anxiety.
Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test
The Novel Object Recognition (NOR) task is used to evaluate cognition, particularly recognition memory in rodent models of Central Nervous System (CNS) disorders. The amount of time taken to explore the novel object reflects the use of learning and recognition memory. This test is useful for assessing impaired cognitive ability in transgenic strains of mice and evaluating novel chemical entities for their effects on cognition.
Epilepsy and Seizure Behavioural Test
In experimental models of epilepsy, the Racine scale is often used to evaluate the stages of epileptic seizures in mice. With the aid of videos and EEG recordings, we can therefore establish which stages of epileptic seizures the mice is having after taking the drugs.
